研究者紹介
Researcher
医学系研究科
生命医科学専攻
MA RUIYA

- 研究テーマResearch theme
- 1.Clinical significance and biological role of EEPD1 in colorectal cancer
2.Study on the anticancer effect of traditional Chinese herbs in the field of gastrointestinal tumors
- 研究内容の概要Overview
- 1.The morbidity and mortality of gastrointestinal tumors are gradually increasing worldwide, posing a threat to human health. Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks third in incidence and second in mortality worldwide, with estimates of more than 1.9 million new CRC cases and 935,000 deaths in 2020. Chemotherapeutic drug resistance and the side effects of chemotherapy make the prognosis of the disease poor. Therefore, the treatment management of CRC is challenging. In our previous research works, Exonuclease /Endonuclease/ Phosphatase Domain-1 (EEPD1) was used as a research target by screening the TCGA database (1-1). EEPD1 is a structure-specific nuclease that mediates DNA repair function and is a potential target for cancer therapy. Replication fork stalling and collapse is a major source of genome instability leading to neoplastic transformation or cell death. Such stressed replication forks can be conservatively repaired and restarted using EEPD1-mediated homologous recombination. Studies of EEPD1 in CRC have not yet been reported. Therefore, I would like to use some series of experiments to explore the expression and clinical prognostic significance of EEPD1 in colorectal cancer and the role of EEPD1 in the regulation of CRC progression (1-2).
5‑Fluorouracil (5‑FU) is the first‑line chemotherapeutic drug in the treatment of CRC. The role of DNA repair in 5-FU response and resistance has been observed in numerous studies. However, its antineoplastic efficiency is limited due to acquired drug resistance. Targeting key genes or signaling pathways involved in drug resistance has the potential as a therapeutic strategy to overcome 5-FU resistance during CRC treatment.
ABCA1 is located on the cell membrane and mediates the efflux of cholesterol and other lipids to lower intracellular cholesterol levels. Previous studies have shown that ABCA1 is an oncogene in colorectal cancer and is also associated with acquired tumor chemoresistance. EEPD1 is a novel LXR target gene in macrophages which promotes cellular cholesterol efflux by controlling cellular levels and activity of ABCA1.
Furthermore, our research group will construct chemotherapeutic drug-resistant cell lines, and if the 5-FU-resistant cell lines are constructed successfully, then I will identify the role of the regulatory relationship between EEPD1 and ABCA1 in colorectal cancer 5-FU resistance.
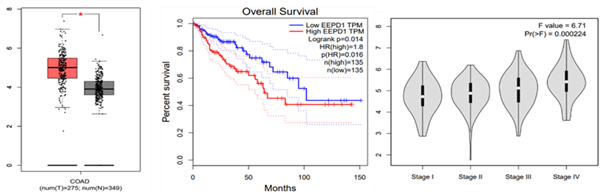
1-1
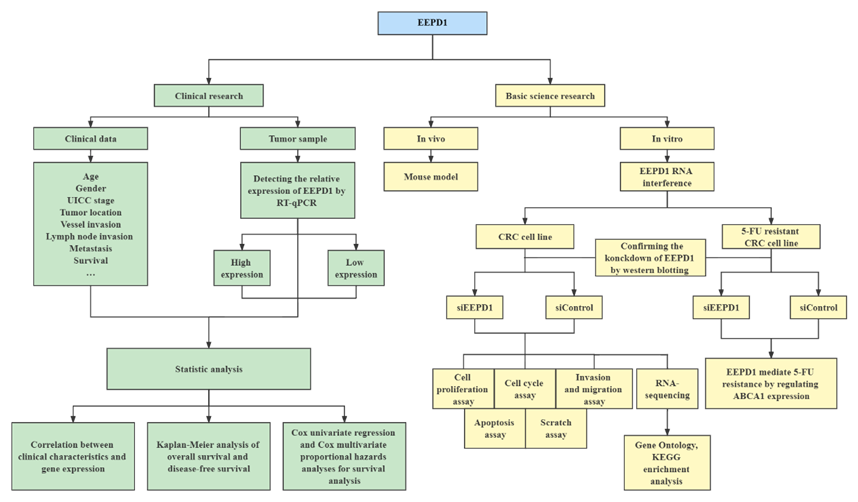
1-2
2.The treatment of gastrointestinal tumors continues to progress, with therapeutic agents and regimens being updated in recent years. The complementary and alternative medicine,
especially dietary compounds, has gained economic and sociological importance because of its cost‑effectiveness and reduced toxicity from chemotherapy drugs. The research of traditional Chinese herbs in the field of cancer is gradually becoming popular, aiming to bring more therapeutic options to patients with gastrointestinal tumors, improve prognosis and enhance the quality of life. I would like to choose from a selection of historical herbs that have not been researched. The anticancer effects of the herb in gastrointestinal tumor cell lines were first explored through a series of in vivo and vitro experiments.
Furthermore, if the chemotherapy drug resistant cell lines are constructed successfully in our laboratory, then I will evaluate whether the herb has the effect to enhance chemotherapy drug cytotoxicity in gastrointestinal tumor cells and investigate whether the herb also act as a chemotherapy drug resistance reversal agent in chemotherapy drug resistant tumor cells.
- 研究成果をどのように社会に役立てるか
(還元の構想)Giving back to society - 1.First, demonstrating that EEPD1 is a prognostic and chemoresistance biomarker of CRC. Second, revealing that the EEPD1/ABCA1 axis plays an important role in the acquisition of 5‑FU resistance in CRC, and targeting EEPD1/ABCA1 may be a promising adjuvant therapeutic strategy for patients with 5‑FU‑resistant CRC. Our results of the research may provide pivotal information for the identification of high-risk CRC patients. In addition, EEPD1 might be a novel therapeutic target in CRC patients.
2.We demonstrating that our target herd exerts its anti‑tumorigenic effects in gastrointestinal tumor cells, indicating that it could serve as an adjunctive therapeutic option in patients with gastrointestinal tumor cells. We have studied the anticancer effects of Andrographis in gastric cancer cells (2-1). Our research providing novel insights into the potential of Andrographis as an adjunctive treatment option for patients with metastatic gastric cancer. As with our previous studies, the herbs we studied are derived from daily food, are safe and affordable. They can provide cancer patients with more choices in treatment and can reduce the side effects of conventional chemotherapy.



